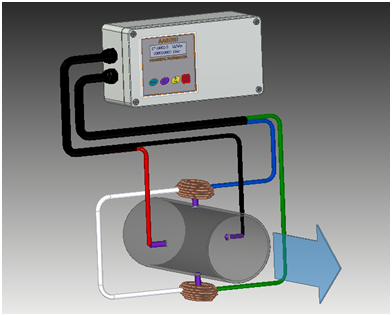
What is Electromagnetic Flowmeter Working Principle?
What is an Electromagnetic Flowmeter
An electromagnetic Flowmeter, simply known as a magnetic flowmeter ( Magmeter, Flowmeter, flow measuring device, Megflow, etc.) is a volumetric flow meter. It is a transducer that measures fluid flow by the voltage induced across the liquid by its flow through a magnetic field.
A magnetic field is applied to the metering or flow tube, which results in a potential difference proportional to the flow velocity perpendicular to the flux lines.
The Flowmeter (Standard Version) can be used for flow measurement in both the direction.
The water flow meter also gives us a DC Current Output in the range of 4-20 mA proportional to flow before delivery the measuring range is set. Indication of the flow and adjust to suit customer requirements.
Recording instruments like current indicators, communication with power panel instruments, and flow rate measuring devices can be connected with Electromagnetic Flowmeter output.

Measuring Principle of Flowmeter
Magnetic flowmeters work based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction.
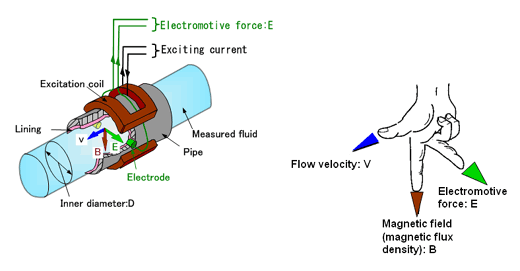
According to this principle, when a conductive medium passes through a magnetic field B, a voltage E is generated which is proportional to the velocity v of the medium, the density of the magnetic field, and the length of the conductor.
In a magnetic flow meter, a current is applied to wire coils mounted within or outside the meter body to generate a magnetic field.
The liquid flowing through the pipe acts as the conductor and this induces a voltage that is proportional to the average flow velocity.
This voltage is detected by sensing electrodes mounted in the Electromagnetic flowmeter body and sent to a transmitter which calculates the volumetric flow rate based on the pipe dimensions.
Mathematically,
we can state Faraday’s law as
E is proportional to V x B x L
where,
E – is the voltage generated in a conductor,
V- is the velocity of the conductor,
B- is the magnetic field strength.
L- is the length of the conductor.
Basic working of Magnetic flowmeter
It is very important that the liquid flow that is to be measured using the magnetic flow meter must be electrically conductive. Faraday’s Law indicates that the signal voltage (E) is dependent on the average liquid velocity (V), the length of the conductor (D), and the magnetic field strength (B).
The Magnetic field will thus be established in the cross-section of the tube. Basically, when the conductive liquid flows through the magnetic field, voltage is induced. To measure this generated voltage (which is proportional to the velocity of the flowing liquid), two stainless steel electrodes are used which are mounted opposite each other.
The two electrodes which are placed inside the flow meter are then connected to an advanced electronic circuit that has the ability to process the signal.
The processed signal is fed into the microprocessor that calculates the volumetric flow of liquid.
To know more watch the below video for a 3D illustration of the flow meter working
Flowmeter Application
The main applications can be found in the following sectors,
- Water and wastewater
- Chemical and pharmaceutical industries
- Food & beverage industry
- Mining and cement industries
- Pulp and paper industry
- Steel industry
- Ceramic industries
- Power generation; utility and chilled water industry
Advantages of flowmeter
There are numerous benefits to using electromagnetic flowmeters to perform fluid flow measurements.
- No moving/rotary parts in line therefore there is no additional pressure losses is generated.
- Only the lining of the pipe wall and the electrodes are in contact with the measured liquid.
- The generated voltage is exact linear function of the average flow velocity.
- The signal from the entire space filled by the magnetic field, it occurs as an average value over the pipe section.
- They can usually measure multidirectional flow, either upstream or downstream.
- No moving/rotary parts in line therefore there is no additional pressure losses is generated.
- Only the lining of the pipe wall and the electrodes are in contact with the measured liquid.
- The generated voltage is exact linear function of the average flow velocity.
- The signal from the entire space filled by the magnetic field, it occurs as an average value over the pipe section.
- They can usually measure multidirectional flow, either upstream or downstream.
- How do you troubleshoot 3 phase AC motor?
 The table presented below provides a comprehensive insight into the…
The table presented below provides a comprehensive insight into the… - Types of losses in Induction Motor
 The losses in induction motor are broadly categorized into two…
The losses in induction motor are broadly categorized into two… - 5 Symptoms Of Failing Electric Motor Rotor
 Motors are used everywhere in industrial environments and they are…
Motors are used everywhere in industrial environments and they are… - Comparison between servo motor vs induction motor
 The Technological lines separating induction motors from servo motors are…
The Technological lines separating induction motors from servo motors are… - Comparison between Electromagnetic Flowmeter and Ultrasonic Flowmeter
 Water and wastewater Expert depends on accurate flow measurements for…
Water and wastewater Expert depends on accurate flow measurements for… - How do IP protection ratings work?
 How do Ingress Protection ratings (IP) work? IP Protection ratings…
How do Ingress Protection ratings (IP) work? IP Protection ratings…