How to Measure the Strength of a Magnet
If you know how to measure the strength of a magnet, you know the value of your investment. magnets come in many strengths, and you can use a gauss meter to determine the strength of a magnet.
You can measure the magnetic field in teslas or the magnetic flux in webers or Teslas • m2 (“tesla square meters”). The magnetic field is the tendency for a magnetic force to be induced on moving charged particles in the presence of these magnetic fields.
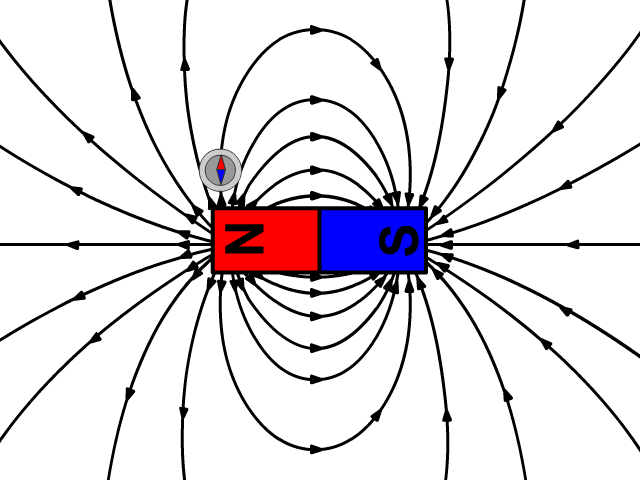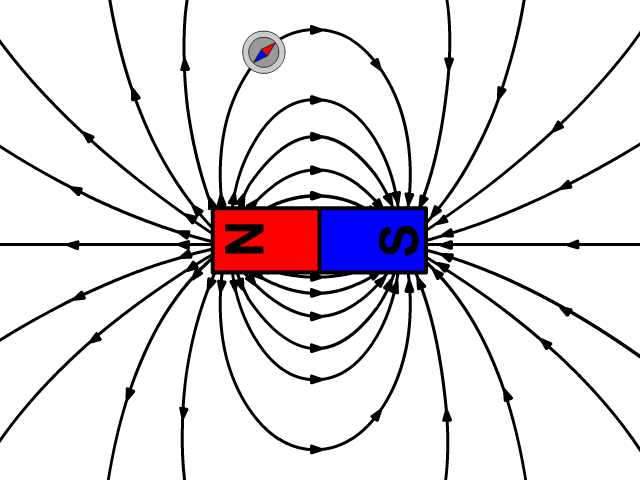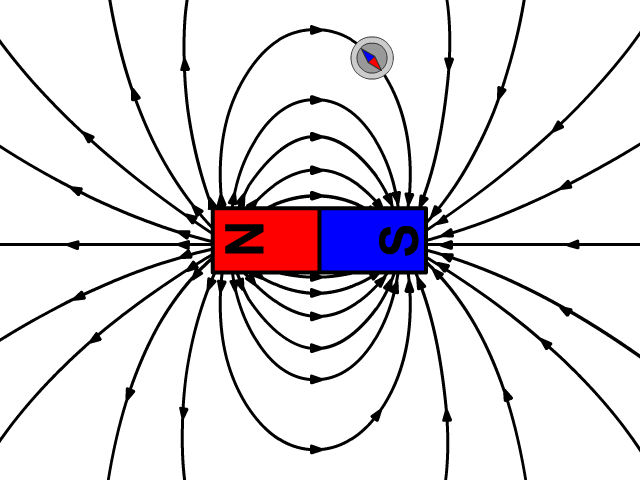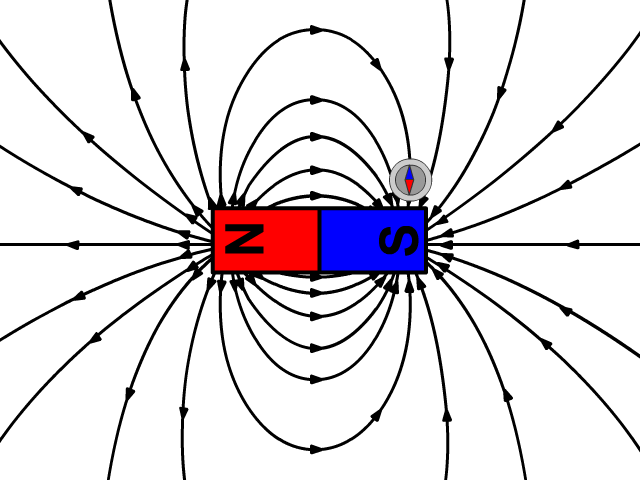
Choosing Magnet by Strength
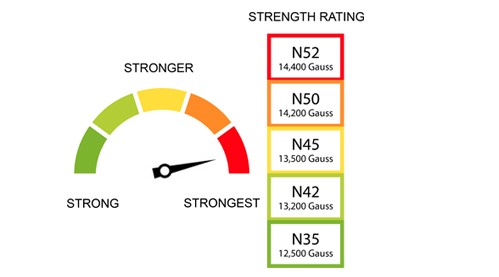
Here’s what magnet grades mean in relation to the strength of your magnets.
A magnet grade is a good measure of the strength of a magnet. In general, higher numbers indicate a stronger magnet.
The number comes from the Maximum Energy Product of the magnet material, expressed in MGOe (Mega Gauss Oersteds).
Neodymium magnets come in different grades, like:
- N42.
- N52.
- N42SH.
What do these numbers mean, and how does the grade relate to the strength of a magnet?
Different magnets address different purposes.
The grade number N52 is the highest possible strength with the smallest possible package at room temperature. N42 is also a common choice that comes at a cost-effective strength, even at high temperatures. At some higher temperatures, N42 magnets may be more powerful than N52 ones with some specialized versions like N42SH magnets designed specifically for hot temperatures.
Be careful when applying magnets in areas of high amounts of heat, though. Heat is a strong factor in demagnetizing magnets. Neodymium magnets generally lose very little strength over time, however.
The pull force from a magnet varies with the grade, or “N” number. A higher N is stronger. Double the N number and you get about double the pull force.
What grade magnet should you use for your application?
The best grade for you depends on your application.
If you need high strength in a tiny package at room temperature, grade N52 is the strongest available. If you want a balance of strength and cost, grade N42 is the sweet spot, with a good balance performance at a range of temperatures for a good price.
If you work in moderately elevated temperatures, around 60°C -80°C, N42 magnets might actually be stronger than N52. This is especially true if your magnet shape is very thin.
Gauss Meter / Tesla Meter
A gauss meter displays electromagnetic wave measurements in Gauss (G), milliGauss (mG), milliTesla (mT) or microTesla (µT) units. A gauss meter can detect either static (DC) permanent (rare-earth) magnetic or dynamic (AC) electromagnetic fields (EMFs), or both.
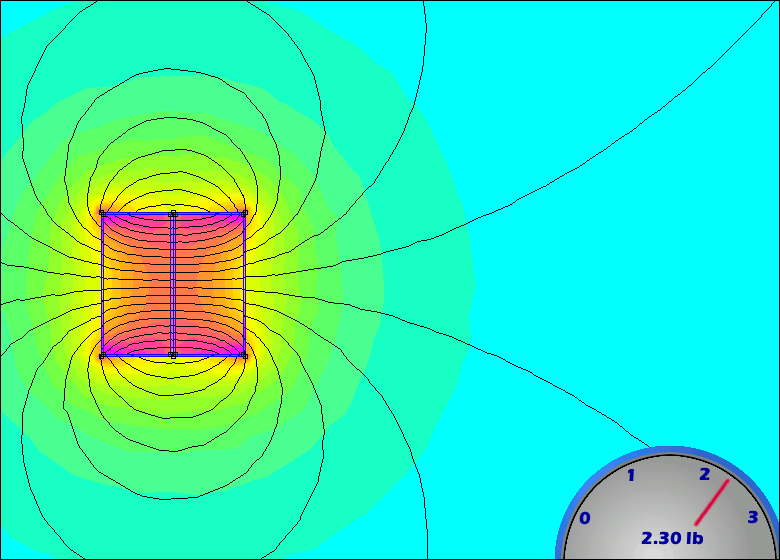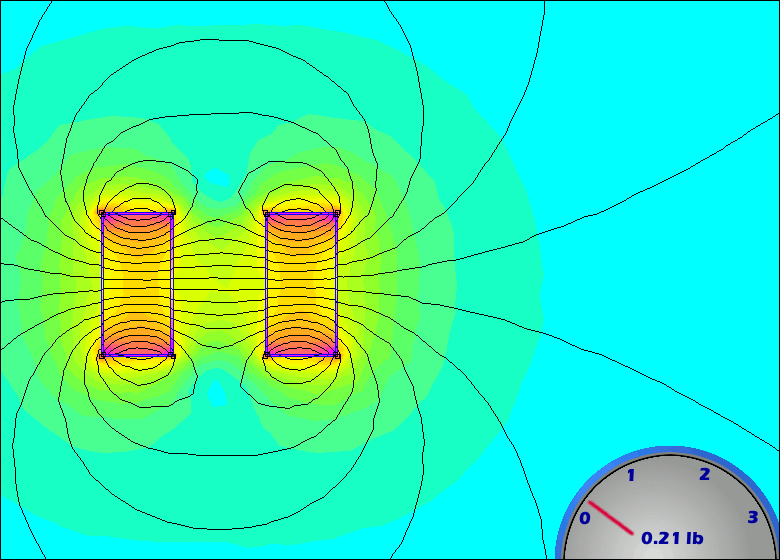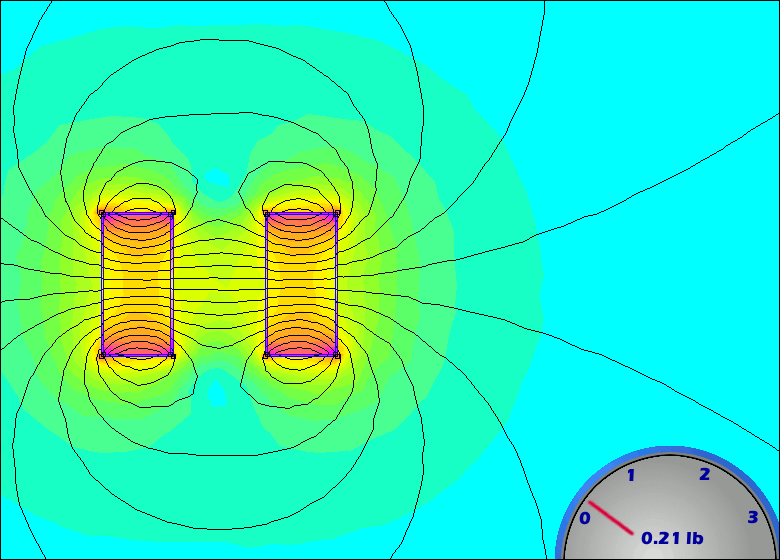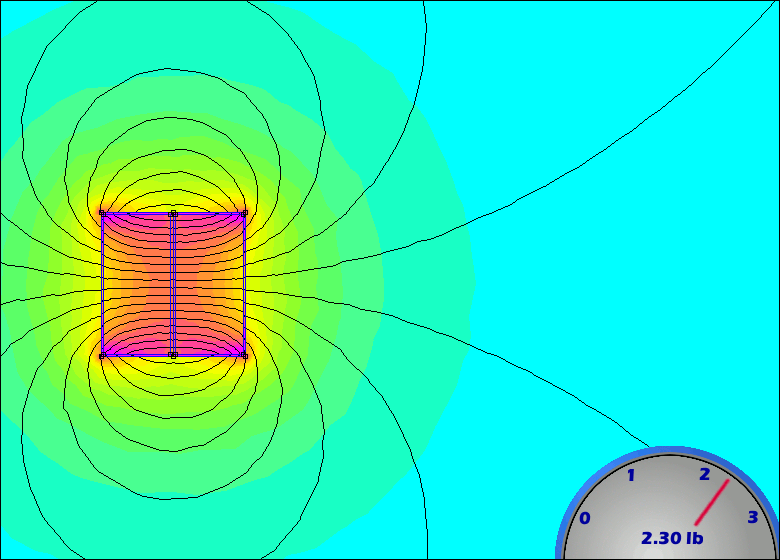
Thus, it is important to review the specifications of a gauss meter prior to purchase to ensure suitability for the intended application.
Neodymium (NdFeB) permanent magnets are among the world’s strongest and most widely used magnets. When testing magnets made of neodymium or other rare-earth elements, a gaussmeter or magnetometer capable of measuring DC magnetic fields is required.
However, most electromagnetic fields encountered are generated by AC currents.
GAUSS MEASUREMENTS IN COMPARISON
- 0.5 Gauss-Earth’s magnetic field at its surface
- 100 Gauss- A typical refrigerator magnet
- 1,100 Gauss – Magnetic rubber grade Y
- 3,700 Gauss -Ferrite(ceramic)magnets
- 11,000 Gauss- Samarium cobalt grade 2:17 magnet
- 12,500 Gauss- Alnico grade 5 magnet
- 13,000 Gauss -Neodymium grade N42 magnet
To know more about various magnet strength measurement technique watch below video.










